Uterine ablation represents a significant advancement in the field of women’s health, offering a minimally invasive solution for a range of gynecological conditions. This innovative medical technology has revolutionized the treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding, a common and often debilitating issue that affects millions of women worldwide. By precisely targeting and destroying the uterine lining (endometrium), uterine ablation procedures aim to significantly reduce or eliminate menstrual bleeding, thereby improving the quality of life for patients.
The development and refinement of uterine ablation techniques highlight the ongoing innovation within medical technology, demonstrating how cutting-edge approaches can offer safer, more effective, and less disruptive alternatives to traditional surgical interventions. This article will delve into the core principles of uterine ablation, explore the various technological approaches employed, discuss the patient experience and benefits, and consider its place within the broader landscape of medical innovation.

The Technological Underpinnings of Uterine Ablation
At its heart, uterine ablation is a technological solution designed to address a specific biological problem: excessive or abnormal uterine bleeding. This bleeding, often stemming from conditions like fibroids, polyps, or hormonal imbalances, can lead to anemia, fatigue, pain, and significant disruption to a woman’s daily life. Traditional treatments, such as hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus), while effective, involve a major surgical procedure with longer recovery times, higher risks, and the permanent loss of reproductive capacity. Uterine ablation, in contrast, offers a targeted and often outpatient approach that preserves the uterus, allowing for future pregnancies in many cases.
The innovation lies in the ability to precisely apply energy to the endometrium, causing it to break down and be reabsorbed by the body. This precision is achieved through various energy sources and delivery systems, each representing a distinct technological pathway to achieve the desired therapeutic outcome. The choice of technology often depends on the specific uterine anatomy, the underlying cause of the bleeding, and the physician’s expertise.
Endometrial Destruction Mechanisms
The fundamental principle of uterine ablation is the controlled destruction of the endometrium. This is achieved by delivering a specific form of energy that generates heat, effectively ablating (destroying) the targeted tissue. The technologies have evolved to optimize this energy delivery for maximum efficacy and minimal collateral damage to surrounding structures.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): This method utilizes radiofrequency energy, a type of electromagnetic wave, to heat and destroy the uterine lining. A specialized device, often a probe or catheter, is inserted into the uterus. This device emits radiofrequency waves that cause the water molecules within the endometrial cells to vibrate, generating heat. This heat effectively ablates the targeted tissue. Systems like the NovSure endometrial ablation system are prominent examples of RFA technology. The energy is delivered in a controlled manner, typically for a short duration, allowing for precise ablation of the endometrium.
-
Hydrothermal Ablation: This technique employs heated saline solution to achieve endometrial ablation. A balloon catheter is inserted into the uterus, and sterile saline is heated to a specific temperature. The heated saline is then circulated within the balloon, which expands to fill the uterine cavity. The sustained heat from the saline gradually ablates the endometrial lining. This method offers a gentler approach, relying on conductive heat transfer.
-
Microwave Ablation: Similar in principle to RFA, microwave ablation uses microwave energy to generate heat within the endometrial tissue. A microwave applicator is inserted into the uterus, and controlled microwave energy is delivered to ablate the endometrium. This technology offers another precise method for tissue destruction.
-
Electrosurgery (Electrocautery): While often considered a more traditional surgical technique, advancements in electrosurgical devices have made them applicable in minimally invasive uterine ablation. Loops or electrodes are used to cut and coaglate tissue by passing electrical current through it. This can be performed hysteroscopically, allowing for direct visualization of the tissue being ablated.
Delivery Systems and Visualization
The effectiveness of uterine ablation is not solely dependent on the energy source but also on the sophisticated delivery systems and visualization tools that accompany these technologies. These elements are crucial for ensuring the procedure is performed safely and accurately.
-
Hysteroscopy: Many uterine ablation procedures are performed under hysteroscopic guidance. Hysteroscopy involves inserting a thin, lighted tube (hysteroscope) with a camera into the uterus. This allows the physician to directly visualize the uterine cavity, identify any abnormalities like fibroids or polyps, and precisely guide the ablation device. The real-time imaging provides invaluable feedback, ensuring that the entire endometrium is treated while avoiding damage to other structures.
-
Minimally Invasive Catheters and Probes: The energy delivery devices are designed as minimally invasive tools, often resembling catheters or probes that can be easily inserted through the cervix. These devices are engineered for ergonomic use by physicians and to deliver energy in a controlled and uniform manner throughout the uterine cavity.
-
Smart Monitoring and Control Systems: Modern ablation devices often incorporate sophisticated monitoring and control systems. These systems allow physicians to precisely regulate the energy output, temperature, and duration of the procedure. Some systems may even have built-in safety mechanisms that automatically adjust or cease energy delivery if certain parameters are exceeded, enhancing patient safety.
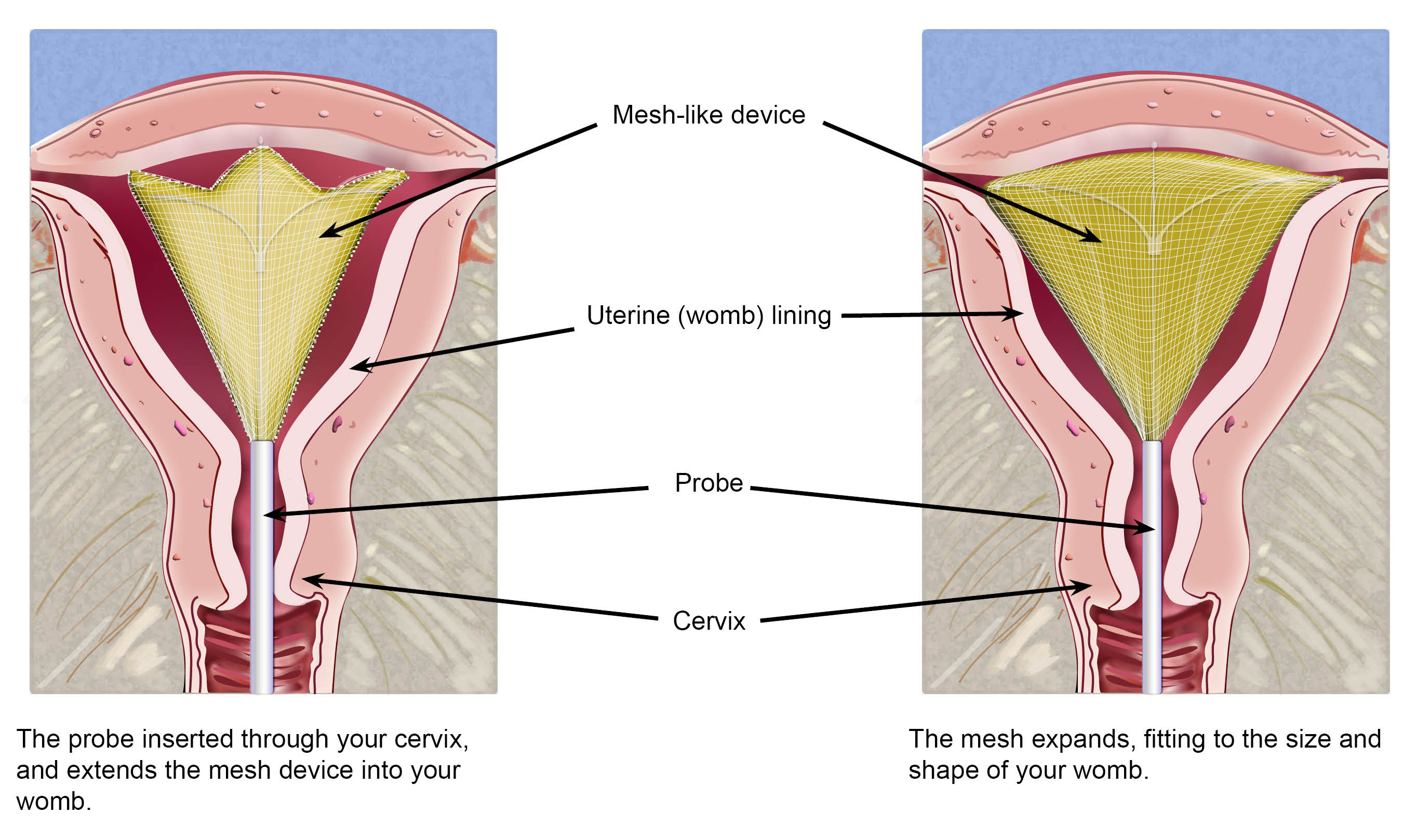
The Patient Experience and Benefits: A Technological Leap Forward
The technological innovations in uterine ablation have profoundly impacted the patient experience, offering significant advantages over traditional surgical interventions. The shift towards minimally invasive approaches represents a major leap forward in gynecological care, prioritizing patient comfort, recovery, and overall well-being.
Minimally Invasive Nature and Reduced Recovery
One of the most significant benefits of uterine ablation is its minimally invasive nature. Unlike hysterectomy, which requires an abdominal incision and several days of hospitalization, most uterine ablation procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis. Patients typically go home the same day or after a very short hospital stay.
This minimally invasive approach directly translates into a significantly reduced recovery period. While some cramping, spotting, and discharge are expected for a few days or weeks following the procedure, most women can return to their normal activities much sooner than with more invasive surgeries. This rapid return to daily life is a testament to the precision and controlled nature of the ablative technologies. The absence of large incisions also means less scarring and a lower risk of infection associated with surgical wounds.
Preservation of the Uterus and Reproductive Potential
A key distinction and advantage of uterine ablation over hysterectomy is the preservation of the uterus. For many women, especially those who have not completed childbearing or who wish to retain their uterus for personal reasons, this is a critical factor. While pregnancy after uterine ablation is not recommended due to potential complications, many women who have undergone the procedure have successfully conceived and carried pregnancies to term in the past. This preservation of reproductive potential is a direct outcome of the targeted approach of endometrial ablation, which aims to remove the lining, not the entire organ.
Efficacy in Treating Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
The primary goal of uterine ablation is to significantly reduce or eliminate abnormal uterine bleeding. Clinical studies and real-world experience have demonstrated high success rates in achieving this outcome. For many women, the procedure leads to a dramatic decrease or complete cessation of menstrual bleeding, effectively resolving the symptoms that had previously impacted their quality of life. This can lead to:
- Reduced Anemia: By controlling excessive blood loss, uterine ablation can help alleviate or prevent anemia, leading to increased energy levels and an improved sense of well-being.
- Elimination of Pain: While not all abnormal bleeding is associated with pain, the reduction in bleeding can often alleviate associated discomfort.
- Improved Quality of Life: Freedom from heavy bleeding, the need for constant management of pads and tampons, and the associated emotional and physical burden significantly improve a woman’s quality of life, allowing them to engage more fully in social, professional, and personal activities.
The Role of Uterine Ablation in Medical Innovation
Uterine ablation stands as a prime example of how technological innovation can directly address unmet needs in healthcare. It represents a paradigm shift from more aggressive surgical interventions to more targeted, less invasive solutions. The evolution of these techniques reflects a broader trend in medicine: the application of advanced technologies to achieve better patient outcomes with fewer side effects and shorter recovery times.
Driving Further Technological Advancements
The success of uterine ablation has spurred continued research and development in gynecological technologies. The pursuit of even more precise, efficient, and patient-friendly methods for managing uterine conditions is ongoing. This includes:
- Refinement of Energy Sources: Ongoing research explores novel energy sources or modifications to existing ones to further optimize tissue ablation and minimize the risk of complications.
- Development of Advanced Imaging and Navigation: Improvements in imaging technologies and real-time navigation systems aim to enhance the precision and safety of these procedures, potentially allowing for more personalized treatment approaches.
- Exploration of Non-Ablative Techniques: While ablation focuses on destroying tissue, future innovations might explore methods to modulate endometrial function without complete destruction, offering alternative therapeutic pathways.

A Model for Minimally Invasive Healthcare
Uterine ablation serves as a powerful model for the broader integration of minimally invasive technologies across various medical specialties. The principles of targeted energy delivery, sophisticated delivery systems, and advanced visualization employed in uterine ablation are transferable to other fields, driving innovation and improving patient care globally. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and less invasive solutions emerge, further enhancing the quality and accessibility of healthcare. The journey of uterine ablation from concept to a widely adopted medical technology underscores the transformative power of innovation in improving human health.
