In an increasingly digital world, our online accounts serve as the gateways to our personal and professional lives. Among these, a Gmail account often stands as a central hub, connecting us to everything from communication and cloud storage to banking, e-commerce, and various app logins. The simple question, “what is my password for my Gmail?”, while seemingly straightforward, unravels a complex tapestry of digital identity, cybersecurity best practices, and the continuous evolution of authentication technologies. This article delves into the critical importance of remembering and managing your Gmail password, the robust recovery mechanisms in place, and the broader innovations shaping the future of digital security, all under the umbrella of Tech & Innovation.
The Imperative of Digital Security: More Than Just a Password
At its core, a password is a secret phrase or string of characters used to verify your identity. For your Gmail account, it’s the primary key to accessing a treasure trove of personal data. Losing or forgetting this key can lead to significant inconvenience, potential data breaches, and even identity theft. Understanding the broader landscape of digital security is paramount, extending beyond mere memorization to proactive strategies for safeguarding your online presence.
Why Strong Passwords Matter
A strong password is your first line of defense. It acts as a barrier against unauthorized access, protecting your emails, documents, photos, and linked services. A strong password is typically:
- Long: Preferably 12 characters or more.
- Complex: A mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Unique: Not used for any other online account.
- Unpredictable: Avoids personal information (names, birthdays) or common dictionary words.
Creating and remembering such passwords can be challenging, but the advent of password managers has revolutionized this aspect, offering secure storage and generation capabilities.
The Ecosystem of Your Digital Life
Your Gmail account is rarely an isolated entity. It often acts as the recovery email for other critical accounts like social media, banking, and professional platforms. This interconnectedness means that compromising your Gmail can lead to a domino effect, granting attackers access to a significant portion of your digital life. Therefore, securing your Gmail isn’t just about your emails; it’s about protecting your entire digital ecosystem. Innovation in tech consistently reminds us that security is not a siloed concept but a holistic approach to managing our online identities.
When Memory Fails: Recovering Your Gmail Account
Despite best intentions, passwords can be forgotten. Google, recognizing the central role Gmail plays for billions of users, has developed a sophisticated and multi-layered account recovery process. This system is designed to verify your identity without requiring the exact password, balancing user accessibility with robust security to prevent malicious takeovers.
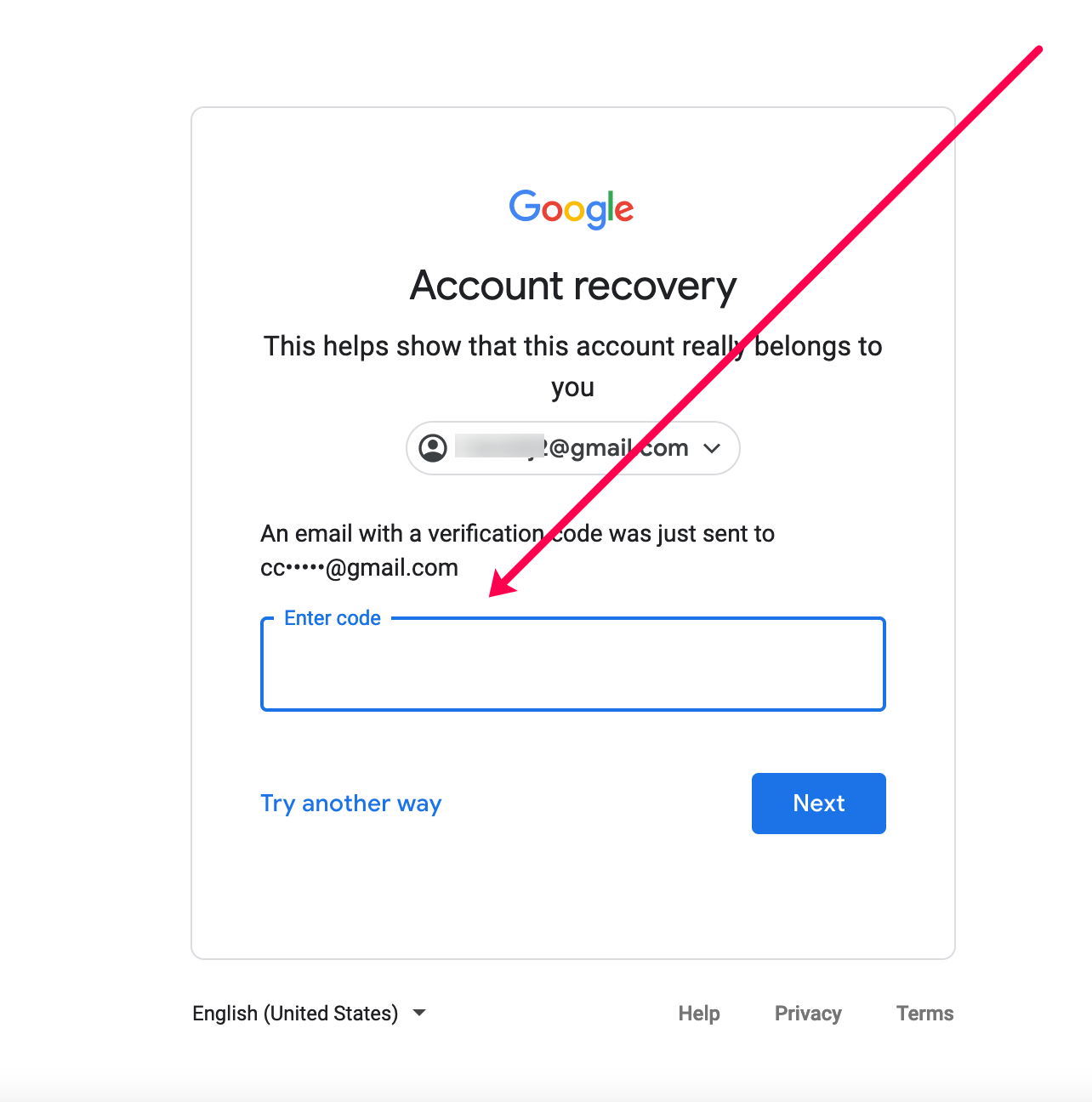
Gmail’s Account Recovery Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you find yourself asking, “what is my password for my Gmail?”, Google’s account recovery page (accounts.google.com/signin/recovery) is your starting point. The process typically involves a series of questions and verification steps designed to confirm you are the legitimate owner:
- Enter your email or phone number: Google first asks for the account you’re trying to recover.
- Provide the last password you remember: Even if it’s incorrect, this helps Google narrow down possibilities.
- Receive a verification code: This is usually sent to a linked phone number or a secondary recovery email address. This step highlights the importance of keeping your recovery information up-to-date.
- Answer security questions: These might include personal questions you set up previously, or queries about when you created the account, or previous contacts you’ve emailed.
- Verify via a trusted device: If you’re attempting recovery from a device you frequently use (e.g., your smartphone or home computer), Google might send a prompt directly to that device for approval, a testament to intelligent authentication mechanisms.
The success of the recovery process heavily depends on the accuracy and completeness of the information you can provide.
Essential Information for Recovery
Proactive setup of recovery options significantly streamlines the process. This includes:
- A recovery phone number: A mobile number where Google can send verification codes via SMS.
- A recovery email address: A secondary email account (not your Gmail) that Google can use for verification.
- Up-to-date contact information: Ensuring your phone number and secondary email are current is crucial.
- Security questions: While less common now with stronger authentication methods, these can still play a role.
Google’s system is constantly innovating, employing machine learning to assess the likelihood that a recovery attempt is legitimate, based on factors like IP address, location, and device history. This innovation ensures that while recovery is possible for legitimate users, it remains difficult for unauthorized parties.
Fortifying Your Digital Gates: Proactive Security Measures
Beyond simply recovering a lost password, the true innovation in tech lies in preventing such incidents and fortifying your accounts against future threats. Google and other tech giants continuously roll out advanced security features, which users are encouraged to adopt.
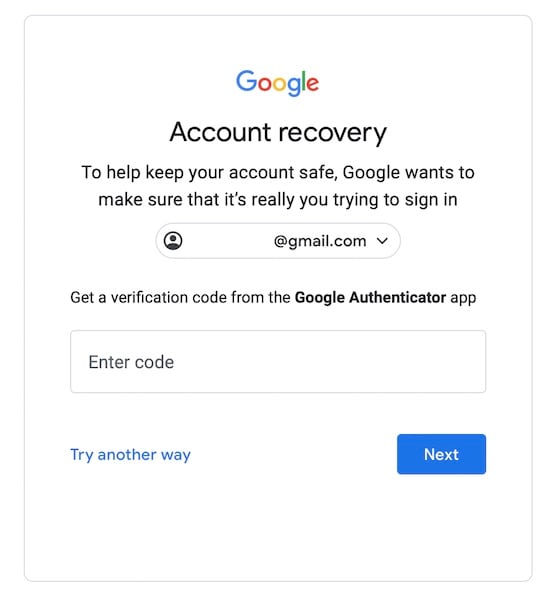
Embracing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Perhaps the single most impactful security measure you can enable is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), also known as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). 2FA adds an extra layer of security beyond just your password. Even if someone obtains your password, they cannot access your account without the second factor. Common second factors include:
- Verification codes: Sent to your phone via SMS or generated by an authenticator app (e.g., Google Authenticator).
- Security keys: Physical USB devices that provide cryptographic proof of identity.
- Biometrics: Fingerprint or facial recognition on a trusted device.
Enabling 2FA for your Gmail account is highly recommended and provides a robust defense against most common hacking attempts. It’s a prime example of how innovation in authentication technology makes our digital lives safer.
Regular Security Check-ups
Google provides a “Security Checkup” tool (myaccount.google.com/security-checkup) that offers a personalized assessment of your account’s security status. This tool allows you to:
- Review recent security activity.
- Manage third-party apps and site access.
- Check your saved passwords for potential breaches.
- Ensure your recovery information is current.
Regularly reviewing these settings ensures that your security posture remains strong and adaptable to new threats. It’s an easy yet effective way to maintain vigilance over your digital identity.
Password Managers: Your Digital Vault
For those struggling to remember strong, unique passwords for every account, password managers are an indispensable piece of modern tech. Services like LastPass, 1Password, Bitwarden, or even Google’s built-in password manager securely store all your complex passwords behind a single master password. They can generate strong, unique passwords for new accounts and autofill login credentials, significantly improving both security and convenience. This innovation alleviates the cognitive load of remembering multiple complex strings, allowing users to adopt best practices effortlessly.
Beyond Passwords: Understanding Advanced Security Threats
While strong passwords and 2FA protect against many threats, the digital landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new challenges to personal security. Understanding these advanced threats is crucial for maintaining a robust defense.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent and effective forms of cyberattack. Attackers attempt to trick you into revealing your login credentials or other sensitive information by impersonating legitimate entities (like Google or your bank) through fake emails, websites, or messages. Social engineering tactics exploit human psychology, manipulating users into making security mistakes. Recognizing the signs of phishing—suspicious links, urgent language, unsolicited requests for personal data—is vital. Google’s advanced spam filters use AI and machine learning to detect and block many phishing attempts, but user vigilance remains the last line of defense.
Data Breaches and Identity Theft
Beyond individual account compromise, large-scale data breaches at websites or services can expose millions of user credentials. Even if you have a strong password, if it’s reused on a site that suffers a breach, your Gmail could be at risk if an attacker tries those credentials. Identity theft, leveraging stolen personal information, can lead to fraudulent activities across various platforms. Staying informed about major breaches and using unique passwords for all accounts are essential mitigations against these broader threats. Tech innovations like Google’s password checkup actively alert users if their saved passwords have appeared in known data breaches.
The Future of Authentication: Innovation in Digital Security
The perennial question of “what is my password?” may one day become obsolete as tech and innovation drive us towards more secure and seamless authentication methods. Researchers and developers are continuously exploring alternatives to traditional passwords, aiming for a future where security is both stronger and less intrusive.
Biometrics and Passwordless Systems
Biometric authentication, utilizing unique physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, offers a convenient and generally secure alternative to passwords. Many modern smartphones and laptops already integrate these technologies. The industry is also moving towards “passwordless” systems, which eliminate the need for traditional passwords altogether. Technologies like FIDO (Fast Identity Online) rely on cryptographic keys stored on your devices, authenticated by a PIN or biometric scan. This approach significantly reduces the risk of phishing and makes account access more streamlined, representing a major leap in digital security innovation.
AI and Machine Learning in Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are at the forefront of modern cybersecurity. These technologies are deployed to:
- Detect anomalous behavior: AI can learn typical user patterns and flag unusual login attempts, geographical access, or device usage that might indicate a compromise.
- Identify sophisticated threats: Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify new malware, zero-day exploits, and advanced phishing techniques that might evade traditional defenses.
- Enhance recovery processes: As mentioned, AI helps Google intelligently assess the legitimacy of account recovery attempts, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access while easing the burden for legitimate owners.
These innovations promise a future where our accounts are not just protected by static passwords but by dynamic, intelligent systems constantly learning and adapting to the evolving threat landscape.
In conclusion, while the question “what is my password for my Gmail?” might stem from a moment of forgetfulness, it serves as a powerful reminder of our ongoing responsibility in the digital age. By understanding Gmail’s robust recovery options, embracing proactive security measures like 2FA and password managers, and staying aware of emerging threats and innovations in authentication technology, we can confidently navigate our digital lives, ensuring our online identities remain secure and accessible. The journey of digital security is one of continuous learning and adaptation, driven by relentless innovation.
