Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) is a comprehensive, high-performance data integration platform developed by Oracle. It is designed to address the complex challenges of extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data across diverse IT environments. In today’s data-driven world, organizations rely on accurate, timely, and consistent data to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge. ODI provides the robust capabilities needed to achieve these goals by enabling seamless data movement and transformation from a multitude of sources to various target systems, including data warehouses, data lakes, operational data stores, and cloud-based applications.
ODI distinguishes itself from traditional ETL tools through its innovative, change data capture (CDC) based approach and its reliance on a declarative, metadata-driven methodology. This approach allows for a more efficient and scalable data integration process, minimizing the need for extensive custom coding and maximizing the utilization of the target system’s processing power. Whether dealing with large volumes of batch data or real-time streaming data, ODI offers a flexible and powerful solution to manage the entire data integration lifecycle.
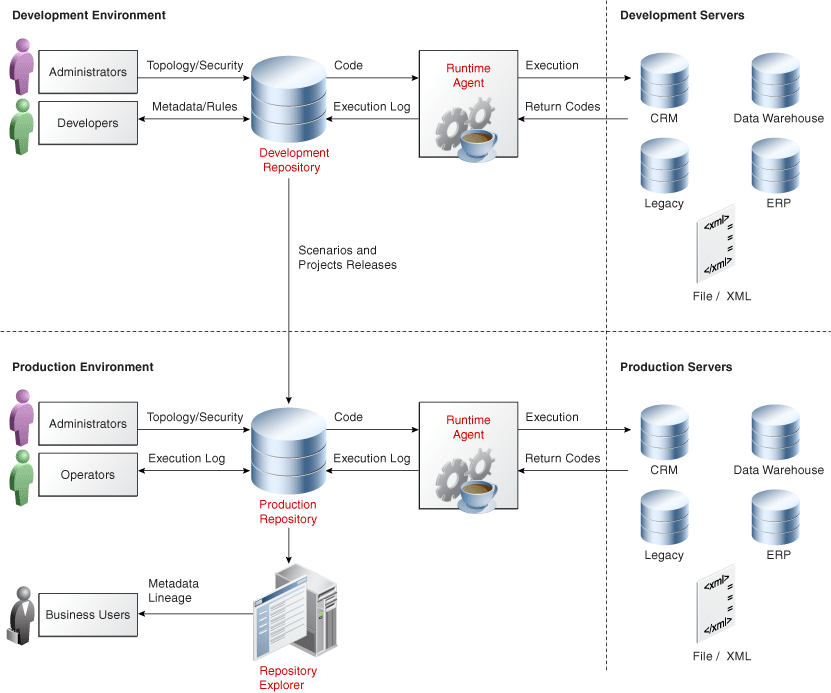
Core Principles and Architecture
At its heart, Oracle Data Integrator is built upon a set of core principles that guide its design and functionality. These principles aim to deliver a highly performant, scalable, and maintainable data integration solution. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial to appreciating ODI’s capabilities and how it solves complex data challenges.
Declarative Design and Metadata-Driven Approach
Unlike many traditional ETL tools that rely heavily on procedural programming, ODI champions a declarative, metadata-driven approach. This means that the integration logic is defined by describing what needs to be done with the data, rather than how to do it step-by-step. All integration processes, transformations, and mappings are stored as metadata within the ODI repository.
- Metadata Repository: The ODI repository is the central hub where all design-time information is stored. This includes details about data sources and targets, data models, mappings, integration flows, and execution logs. By storing everything as metadata, ODI offers significant advantages in terms of reusability, maintainability, and adaptability. Changes to data structures or integration requirements can be managed efficiently by modifying the metadata, rather than rewriting complex code.
- Declarative Rules: Integration logic is expressed through declarative rules. For example, instead of writing SQL code to join tables, you define a join condition in the mapping. ODI then generates the most efficient SQL code to execute this join on the target system. This promotes abstraction, allowing developers to focus on the business logic of data integration rather than the intricacies of different database dialects.
Leveraging Target System Power
A key differentiator of ODI is its ability to push transformation logic to the source or target systems, rather than relying on a separate ETL engine to perform all transformations. This “ELT” (Extract, Load, Transform) or “E-LT” approach maximizes the use of the processing power of the target data management systems, which are often optimized for large-scale data processing.
- In-Memory Transformations: ODI can perform transformations directly within the source or target database, leveraging their native SQL capabilities. This significantly reduces data movement across the network, leading to faster execution times and lower resource consumption. For instance, when transforming data destined for a data warehouse, ODI will generate SQL statements that are executed directly by the data warehouse, rather than moving the data to a staging server for transformation.
- Knowledge Modules (KMs): ODI’s intelligence in leveraging target systems is powered by Knowledge Modules (KMs). KMs are pre-built, pluggable components that contain the code templates and logic to generate optimized SQL for specific technologies and integration scenarios. Oracle provides a wide array of KMs for various databases, data warehouses, big data platforms, and cloud services. Users can also develop custom KMs to support proprietary technologies or unique integration requirements.
Change Data Capture (CDC)
Oracle Data Integrator incorporates a robust Change Data Capture (CDC) mechanism, which is critical for efficient incremental data integration. Instead of re-processing entire datasets, CDC identifies and processes only the data that has changed since the last integration cycle.
- Efficient Incremental Loads: CDC dramatically reduces the volume of data that needs to be processed, leading to significant performance improvements, especially for large and frequently updated datasets. This is crucial for maintaining up-to-date data in data warehouses and operational systems.
- Real-time and Near Real-time Integration: ODI’s CDC capabilities enable near real-time or real-time data synchronization, allowing organizations to react quickly to business events and maintain current data across their systems. This is invaluable for operational reporting, fraud detection, and other time-sensitive applications.
Key Components and Functionality
Oracle Data Integrator is a modular platform, comprising several key components that work together to deliver a complete data integration solution. Understanding these components provides insight into how ODI is designed, developed, and deployed.
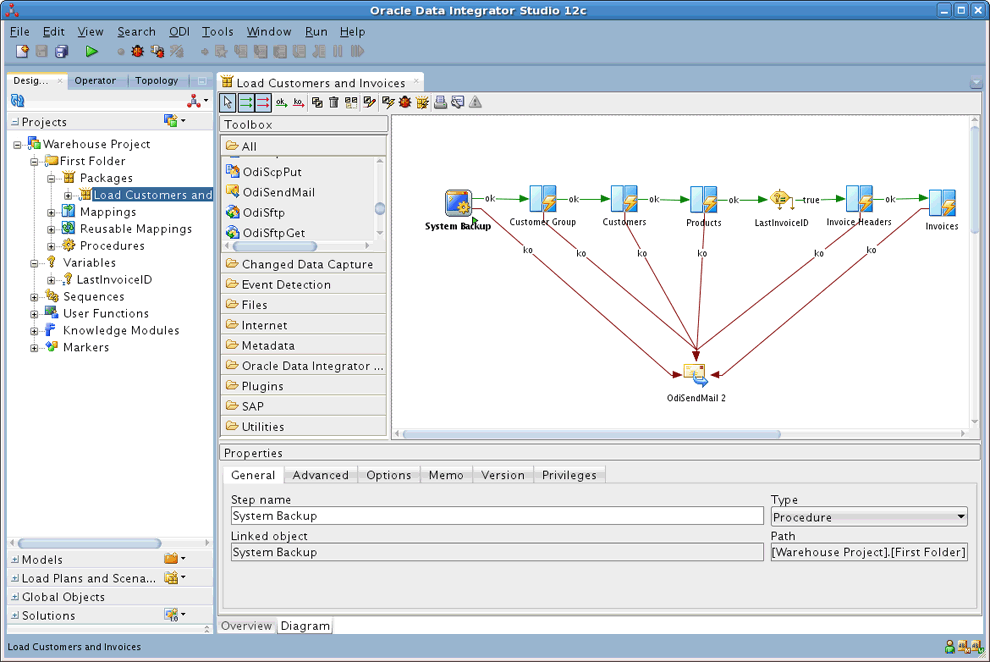
Oracle Data Integrator Studio
ODI Studio is the primary graphical development environment for designing and managing ODI integration processes. It provides a user-friendly interface for all design-time activities, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy their data integration solutions.
- Topology Navigator: This section of ODI Studio is used to define and manage the physical and logical connections to all data sources and targets. It allows for the configuration of technologies, data servers, schemas, and physical and logical data schemas. This centralized view ensures consistency and accuracy in data source definitions.
- Model Navigator: Within the Model Navigator, developers define and manage data models. This involves importing tables, columns, and constraints from physical schemas, defining data types, and establishing relationships between tables. ODI uses these models to understand the structure of the data it will be integrating.
- Navigator: This is the core design area where data integration processes are created. Here, developers design mappings, load plans, procedures, and other integration artifacts. Mappings define how data is extracted from sources, transformed, and loaded into targets, utilizing KMs to generate optimized code.
- Performance Tuning and Debugging Tools: ODI Studio includes integrated tools for performance monitoring and debugging. Developers can analyze execution logs, identify performance bottlenecks, and step through integration processes to troubleshoot issues effectively.
ODI Repository
The ODI Repository is the central metadata store that holds all design-time and runtime information for an ODI installation. It is typically implemented using Oracle Database schemas.
- Development Repository: Stores all the design-time metadata, including models, mappings, procedures, KMs, and integration project definitions. This is where developers work to build their integration solutions.
- Runtime Repository: Stores runtime information such as execution logs, error messages, performance statistics, and tracer information. This repository is essential for monitoring and managing executed integration processes.
Repository (Optional): A separate repository for storing user and security information, offering enhanced security management.
Oracle Data Quality (DQ)

While not strictly an ODI component, Oracle Data Quality is often integrated with ODI to ensure the accuracy and consistency of data throughout the integration process.
- Data Profiling: ODI can be used to profile data to understand its characteristics, identify anomalies, and assess its quality. This profiling information can then be used to define data quality rules.
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Through integration with Oracle Data Quality tools or custom procedures, ODI can perform data cleansing, standardization, and de-duplication to ensure that the data loaded into target systems is accurate and conforms to defined standards.
Oracle Data Integrator Agent
The ODI Agent is the runtime component responsible for executing the integration processes. It is a Java-based application that runs on the server where the integration jobs are executed.
- Connectivity and Execution: The Agent connects to the various data sources and targets defined in the Topology, retrieves data, executes transformations, and loads data according to the designs defined in ODI Studio.
- Scalability and High Availability: ODI Agents can be configured in a standalone mode or as part of a clustered environment to provide scalability and high availability, ensuring that data integration processes can run reliably even under heavy load.
- Jython and Groovy Scripting: Agents can execute custom scripts written in Jython or Groovy, allowing for advanced customization and integration with external systems or complex business logic.
Advanced Features and Use Cases
Oracle Data Integrator offers a rich set of advanced features that cater to a wide range of complex data integration scenarios, from big data processing to cloud migration and real-time analytics. These capabilities empower organizations to tackle their most demanding data challenges.
Big Data Integration
In the era of big data, ODI provides robust capabilities for integrating data from various big data platforms.
- Hadoop Integration: ODI can seamlessly integrate with Hadoop ecosystems, including HDFS, Hive, and Spark. It can read data from Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), execute transformations using Hive or Spark SQL, and load data back into Hadoop or other target systems. This enables organizations to leverage their big data assets for analytics and business intelligence.
- NoSQL Integration: ODI also supports integration with various NoSQL databases, allowing for the extraction, transformation, and loading of data from document stores, key-value stores, and other non-relational data sources.
Cloud Data Integration
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud strategies, ODI facilitates seamless data integration between on-premises systems and cloud applications and data stores.
- Cloud Platform Connectors: ODI offers connectors for popular cloud platforms such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure. This allows for the efficient movement of data to and from cloud-based data warehouses (e.g., Snowflake, Redshift, BigQuery), data lakes, and SaaS applications.
- Hybrid Cloud Scenarios: ODI is ideal for hybrid cloud environments, enabling organizations to integrate data across both their on-premises infrastructure and their cloud deployments, providing a unified view of their data assets.
Real-time Data Synchronization and Streaming
ODI’s CDC capabilities extend to near real-time data synchronization, which is crucial for applications requiring up-to-the-minute data.
- Transactional Data Integration: For scenarios like point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, or financial transactions, ODI can capture changes in near real-time and propagate them to target systems, ensuring that analytical and operational systems are always up-to-date.
- Integration with Streaming Technologies: While ODI’s core strength lies in batch and incremental processing, it can be integrated with streaming technologies like Oracle GoldenGate or Kafka to create comprehensive real-time data pipelines.
Data Governance and Compliance
Effective data governance is paramount for ensuring data quality, security, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Audit Trails and Lineage: ODI provides comprehensive logging and auditing capabilities, allowing organizations to track the movement and transformation of data, which is essential for compliance and data governance initiatives. Data lineage features help in understanding the origin and journey of data.
- Data Masking and Security: While ODI itself may not be a dedicated data masking tool, it can be used in conjunction with other Oracle security products or custom scripts to implement data masking and anonymization techniques for sensitive data, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Enterprise Data Warehousing (EDW) and Business Intelligence (BI)
ODI is a cornerstone for building and maintaining robust Enterprise Data Warehouses and powering Business Intelligence solutions.
- Data Warehouse Design and ETL: ODI’s ability to generate highly optimized SQL for target data warehouses makes it an excellent choice for populating complex EDW structures. It handles the extraction of data from various transactional systems, its transformation according to business rules, and its loading into dimensional models.
- BI Platform Integration: By providing clean, consistent, and up-to-date data, ODI ensures that BI platforms have reliable data sources for reporting, dashboarding, and advanced analytics, enabling better decision-making across the organization.
In conclusion, Oracle Data Integrator is a powerful and versatile data integration platform that addresses the modern challenges of data management. Its declarative, metadata-driven approach, combined with its ability to leverage target system power and advanced features like CDC and big data integration, makes it an indispensable tool for organizations looking to unlock the full potential of their data. From complex ETL processes to real-time synchronization and cloud migration, ODI provides the agility and performance required to navigate the ever-evolving data landscape.
