This article will explore the significance of W-2 Box 1, a crucial piece of information on the wage and tax statement every employee receives annually. We will delve into what this specific box represents, why it is vital for tax preparation, and how it differs from other important figures on the W-2.
Understanding the Basics of Your W-2 Form
The W-2 form, officially known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is a document provided by your employer to you and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It summarizes your annual earnings and the amount of taxes withheld from your paychecks. This document is fundamental for accurately filing your federal and state income tax returns. Without it, you would struggle to report your income correctly and claim any applicable tax credits or deductions.

The Purpose of the W-2 Form
The primary purpose of the W-2 form is to create a standardized and verifiable record of your employment income and tax contributions. Employers are legally obligated to furnish W-2 forms to their employees by January 31st of the following year. This ensures that taxpayers have sufficient time to prepare and file their tax returns before the annual deadline, typically April 15th. The IRS also receives a copy of your W-2, allowing them to cross-reference the information reported by employers with what individuals declare on their tax returns, thus aiding in tax compliance.
Key Information Found on a W-2
Beyond Box 1, the W-2 form contains a wealth of information vital for tax filing. These include:
- Employer’s Information: Identification details of your employer, including their name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Employee’s Information: Your personal details, such as your name, address, and Social Security Number (SSN).
- Wages and Tips: Various boxes detailing different types of compensation.
- Tax Withholdings: Boxes indicating the amounts of federal income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, and state/local taxes withheld.
- Benefits and Contributions: Information regarding retirement plan contributions, health savings accounts (HSAs), and other employer-provided benefits.
Each box on the W-2 form serves a specific purpose, and understanding these distinctions is paramount to accurate tax filing.
Deciphering W-2 Box 1: Your Taxable Wages
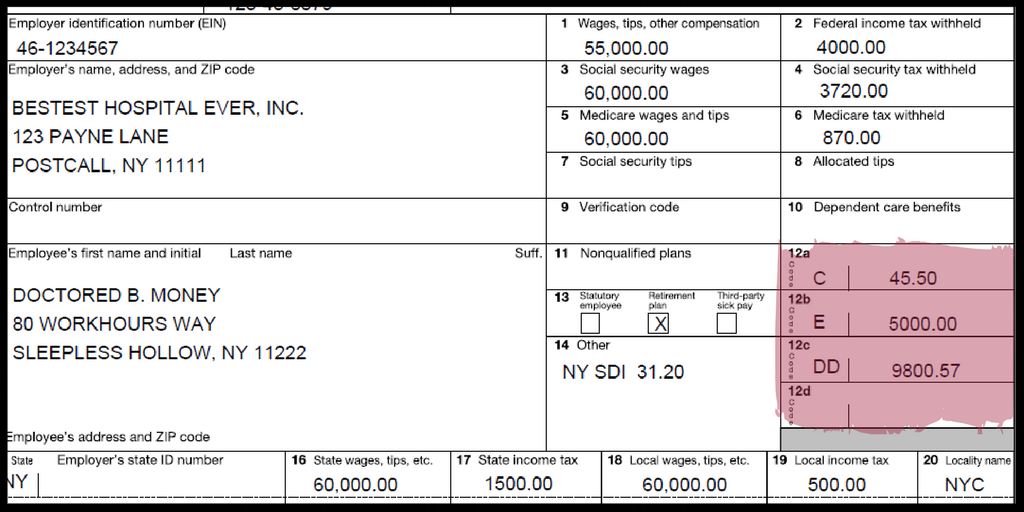
W-2 Box 1 is arguably the most critical box on the entire form. It reports the amount of wages, tips, and other compensation that is subject to federal income tax. This figure is the foundation upon which your federal income tax liability is calculated.
What Constitutes Taxable Wages in Box 1?
The amount reported in Box 1 represents your gross wages, minus any pre-tax deductions. Pre-tax deductions are amounts subtracted from your paycheck before federal income tax is calculated. Common examples of pre-tax deductions include:
- 401(k) or 403(b) Contributions: Contributions you make to employer-sponsored retirement plans reduce your taxable income.
- Health Insurance Premiums: Premiums paid for employer-sponsored health insurance plans are typically deducted on a pre-tax basis.
- Flexible Spending Account (FSA) Contributions: Funds contributed to an FSA for healthcare or dependent care expenses are also usually pre-tax.
- Commuter Benefits: Contributions to programs that subsidize public transportation or parking expenses can be pre-tax.
It’s important to note that the exact components included in Box 1 can vary slightly depending on your specific employment situation and the deductions you have elected. However, the general principle remains: Box 1 reflects the income that the IRS considers taxable for federal income tax purposes.
Why Box 1 is Crucial for Your Tax Return
Your federal income tax return is primarily based on your total taxable income. Box 1 of your W-2 directly feeds into this calculation. When you file your tax return, you will report the amount from Box 1 as your wages on the relevant lines of your Form 1040. This figure is then used to determine your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI), a critical step in calculating your overall tax liability.
Furthermore, various tax credits and deductions are often calculated as a percentage of your income. Therefore, an accurate figure in Box 1 ensures that these calculations are performed correctly, potentially leading to a larger refund or a lower tax bill. Conversely, an error in Box 1 can lead to an inaccurate tax return, potentially resulting in penalties or missed opportunities for tax savings.
Distinguishing Box 1 from Other Key W-2 Figures
While Box 1 is central to your federal income tax calculation, it is essential to understand that it is not the only important figure on your W-2. Several other boxes provide crucial information for different aspects of your tax filing. Understanding these distinctions helps prevent confusion and ensures accurate reporting.
Box 2: Federal Income Tax Withheld
Box 2 reports the total amount of federal income tax that your employer has already withheld from your paychecks throughout the year. This amount is credited against your total tax liability when you file your tax return. If the amount withheld in Box 2 is more than your total tax liability, you will receive a refund. If it’s less, you will owe additional taxes. This figure is directly related to Box 1, as the amount withheld is typically a percentage of the taxable wages reported in Box 1, based on the withholding allowances you claimed on your Form W-4.
Box 3: Social Security Wages
Box 3 shows the total wages subject to Social Security tax. This amount is different from Box 1 because there is an annual limit on the amount of earnings subject to Social Security tax. For instance, if you earn significantly more than the Social Security wage base in a given year, the amount in Box 3 will be capped at that limit, while Box 1 will reflect your full taxable wages. The Social Security tax rate is applied to the amount in Box 3.
Box 5: Medicare Wages and Tips
Box 5 reports the total wages and tips subject to Medicare tax. Unlike Social Security tax, there is generally no annual wage base limit for Medicare tax. Therefore, the amount in Box 5 is usually the same as, or very close to, the amount in Box 1, assuming you have no other specific Medicare tax exclusions. The Medicare tax rate is applied to the amount in Box 5.
Box 6: Medicare Tax Withheld
Box 6 indicates the total Medicare tax that your employer has withheld from your paychecks. This amount, along with the federal income tax withheld (Box 2) and Social Security tax withheld (which is not explicitly shown in a single box but is derived from Box 4), contributes to the total tax payments you have made towards your annual tax obligation.
Navigating Common Issues and Errors Related to Box 1
Errors or misunderstandings regarding W-2 Box 1 can lead to significant problems with your tax return. Being aware of common issues and knowing how to address them can save you time, stress, and potential financial penalties.
What to Do If Box 1 Seems Incorrect
If you review your W-2 and believe the amount in Box 1 does not accurately reflect your taxable wages, the first step is to contact your employer’s payroll or HR department. They can investigate the discrepancy. Possible reasons for an incorrect figure include:
- Incorrect Calculation of Pre-Tax Deductions: An error in how your pre-tax deductions were processed could lead to an inflated or deflated taxable wage amount.
- Misclassification of Income: Certain types of compensation might be misclassified, affecting their taxability.
- Data Entry Errors: Simple human error during data input can occur.
Your employer is responsible for issuing a corrected W-2 form, typically a W-2c, if an error is found. You should not file your tax return with an incorrect W-2; wait for the corrected document.
The Impact of Box 1 on Tax Filing Software and Professionals
Tax filing software and tax professionals rely heavily on the information provided on your W-2. When you input your W-2 details into tax software, the program will use the figures from each box to populate the relevant sections of your tax return. Similarly, tax professionals use this document as the primary source of your income and withholding information. An accurate Box 1 figure is crucial for these tools to perform their calculations correctly. If Box 1 is inaccurate, the software or professional may calculate your tax liability incorrectly, potentially leading to underpayment or overpayment of taxes.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Precise Box 1
W-2 Box 1 is more than just a number; it’s a fundamental indicator of your taxable income for federal income tax purposes. Understanding its contents and how it interacts with other parts of your W-2 form is essential for accurate tax filing and ensuring you meet your obligations while taking advantage of all legitimate tax benefits. By paying close attention to this and other key figures on your W-2, you can navigate the tax season with greater confidence and accuracy.
